Femoral endarterectomy is a surgical procedure carried out to treat blockage of blood flow in the femoral artery. The femoral arteries are blood vessels in the groin area that carry blood to the legs. The femoral arteries may become blocked by fatty tissues thereby leading to difficulty in walking and could potentially results in stroke.
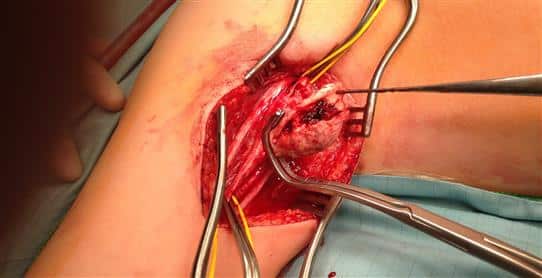
femoral endarterectomy
Indications of femoral endarterectomy
Femoral endarterectomy is indicated when the femoral arteries become blocked by fatty deposits referred to as plaque which causes the patient to experience aching pain during walking. If blood flow is completely blocked, tissue can die.
Most often, other non-invasive treatments such as angioplasty have proved abortive.
Femoral endarterectomy procedure
The of the procedure is to remove the occlusive atherosclerotic plaque together/en masse with a portion of the arterial wall in order to restore blood supply to the tissues
It can be carried out under local anesthesia or general anesthesia. During the procedure, the artery is exposed, and an arteriotomy is created.
The plaque, along with the adherent endothelium and inner tunica media, is elevated off the deeper tunica media layer and extracted out of the arteriotomy wound. The arteriotomy wound is closed using sutures or a patch.
Patient will stay in hospital 1 or 2 nights following this procedure.
Femoral endarterectomy risks and complications
Although, major complications are not common, as with any surgical procedure, there are risks of complications with femoral endarterectomy as in:
- Bleeding – Following femoral endarterectomy, bleeding can occur due to damage to either the artery or the femoral vein or its branches, and may require blood transfusion.
- Anesthetic risks – Includes damage to the teeth, throat and larynx, reaction to medications, nausea and vomiting, cardiovascular and respiratory complications.
- Infection – Superficial wound infection is possible, yet graft infections are also possible and are major complication that require life-long antibiotics and graft excision if possible.
- Seroma – A swelling of lymphatic fluid may occur particularly in the groin due to disruption of the lymph nodes and channels.
Femoral endarterectomy outcomes
You should be able to eat and drink normally once fully awake following your surgery.
Once you are up and about, you should be able to leave hospital, but may need painkilling tablets for up to a month. It can be normal to make a full recovery in about 2 weeks from a femoral endarterectomy.
The long-term result is often good, with the narrowing in the artery repaired for many years.
Read More: Types of Hip Sugery