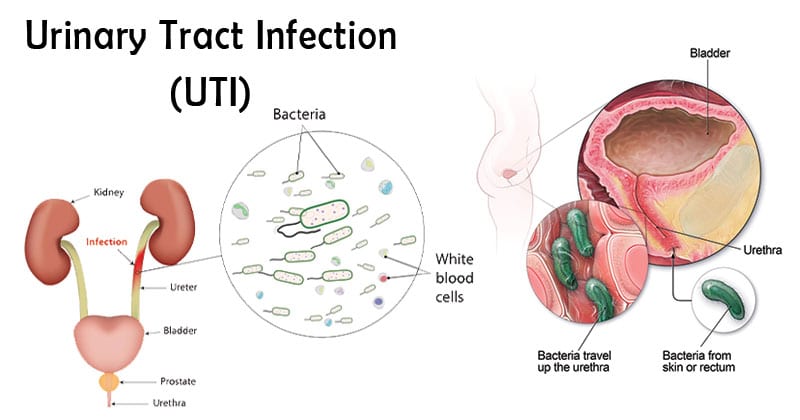
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects the urinary tract which consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
The role of the urinary tract is to make and stores urine. Urine is one of the waste products of your body. Urine is made in the kidneys and travels down the ureters to the bladder. The bladder stores the urine until it is emptied by urinating through the urethra, a tube that connects the bladder to the skin.
There are different types of urinary tract infections depending on the location of the infection.
Symptoms of urinary tract infections generally include pain with urination, frequent urination and fever.
Urinary tract infections are mostly caused by the bacteria Escherichia coli, though other bacteria or fungi may sometimes be the cause.
types of urinary tract infections
Types of Urinary Tract Infections
There are four different types of urinary tract infections. The type of infection depends on which part of the urinary tract is infected.
A urinary tract infection may involve different sections of the urinary tract including the following:
1. Urethritis
Urethritis is an infection of the urethra, the hollow tube that drains urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
Pain with urination is the main symptom of urethritis. Urethritis is commonly due to infection by bacteria. It can typically be cured with antibiotics.
Urethritis causes
Most episodes of urethritis are caused by infection by bacteria that enter the urethra from the skin around the urethra’s opening. Bacteria that commonly cause urethritis include:
- Gonococcus, which is sexually transmitted and causes gonorrhea.
- Chlamydia trachomatis, which is sexually transmitted and causes chlamydia.
- Bacteria in and around the stool.
The herpes simplex virus (HSV-1 and HSV-2) can also cause urethritis. Trichomonas is another cause of urethritis. It is a single-celled organism that is sexually transmitted.
Sexually transmitted infections like gonorrhea and chlamydia are usually confined to the urethra.
2. Cystitis
Cystitis is the most common type of urinary tract infection (UTI). It is the infection of the bladder, the organ that collects and stores urine before disposal by urination.
The condition can result when naturally occurring bacteria in your body become imbalanced. These bacteria lead to an infection and cause inflammation.
Cystitis does not always come from an infection. For example, certain medicines and hygiene products can also cause inflammation.
There are different types of cystitis depending on the cause. They include:
– bacteria cystitis: which occurs when bacteria is the cause of the infection
– drug-induced cystitis: when certain medications cause the bladder to become inflamed
– radiation cystitis: when cystitis results from harmful effects of radiation from radiotherapy
– chemical cystitis: when cystitis results from certain hygiene products such as feminine sprays, spermicidal jellies, chemicals from a bubble bath, etc.
3. Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is inflammation of the kidney, typically due to a bacterial infection. Symptoms most often include fever and flank tenderness.
Pyelonephritis may be acute or chronic. Acute pyelonephritis is a sudden and severe kidney infection. It causes the kidneys to swell and may permanently damage them. Pyelonephritis can be life-threatening.
When repeated or persistent attacks occur, the condition is called chronic pyelonephritis. The chronic form is rare, but it happens more often in children or people with urinary obstructions.
More: Kidney stone treatment
4. Vaginitis
This is another type of urinary tract infection. Vaginitis is an inflammation of the vagina that can result in discharge, itching and pain.
The cause is usually a change in the normal balance of vaginal bacteria or an infection. Reduced estrogen levels after menopause and some skin disorders can also cause vaginitis.
The most common types of vaginitis are:
- Bacterial vaginosis, which results from a change of the normal bacteria found in your vagina to overgrowth of other organisms
- Yeast infections, which are usually caused by a naturally occurring fungus called Candida albicans
- Trichomoniasis, which is caused by a parasite and is commonly transmitted by sexual intercourse
Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections
The mainstay of treatment is antibiotics. Phenazopyridine is occasionally prescribed during the first few days in addition to antibiotics to help with the burning and urgency sometimes felt during a bladder infection.
However, it is not routinely recommended due to safety concerns with its use, specifically an elevated risk of methemoglobinemia (higher than normal level of methemoglobin in the blood). Acetaminophen (paracetamol) may be used for fevers.
More: Inguinal hernia surgery