Hip surgery is a surgical operation that is performed on the hip region and most especially the hip joint to treat hip pain from arthritis and hip fractures.
Depending on each patient’s pathological condition and physical presentation several different types of hip surgery could be utilized. Listed below are types of hip surgery that are commonly being performed to treat orthopedic hip conditions.
Hip Replacement Surgery
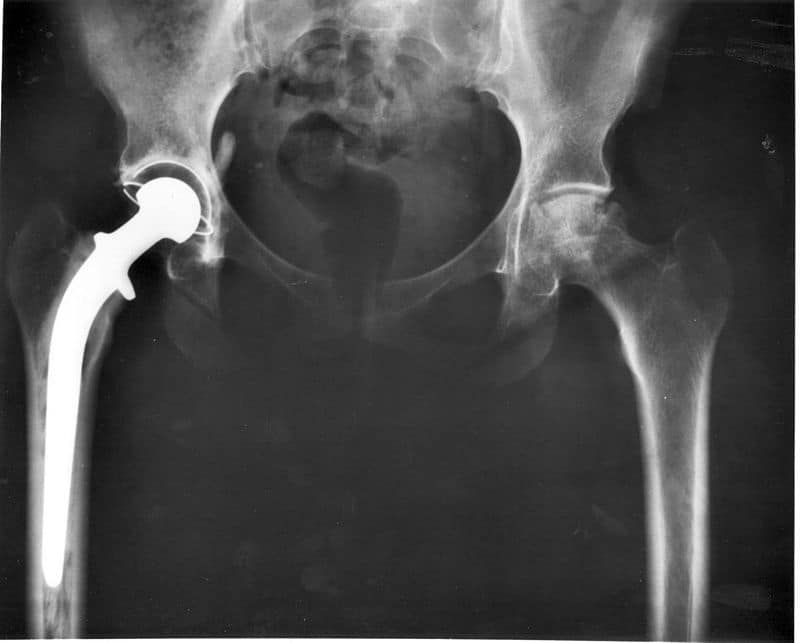
Hip replacement surgery is a surgical procedure in which the hip joint is replaced by a prosthetic implant known as a hip prosthesis. As in knee replacement surgery, it is performed to relieve arthritis pains and discomfort. The aims of the procedure are pain relief and improvement in hip function. Hip replacement is usually considered only after other therapies, such as physical therapy and pain medications, have failed.
There are two types of hip replacement surgery namely: Total hip replacement surgery and Hemi (half) replacement depending on the degree of replacement.
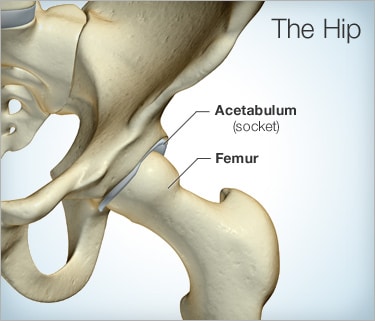
Total hip replacement, also known as total hip arthroplasty, involves the replacement of both the acetabulum (socket) and the femoral head (ball) while hemiarthroplasty only replaces the femoral head (ball).
The two main approaches to performing these surgeries include the anterior approach and the posterior approach.
Posterior approach
This type of hip surgery involves the surgeon creating a 4-6 in (maybe larger for larger patients) incision along the outer buttock, the splitting of the gluteus maximus muscle, and the detaching (and later reattaching of the piriformis muscle and the superior gemeli muscle (2 hip rotator muscles).
The head of the femur is removed and a metal stem is placed in the hollow part of the femur, followed by the placement of metal or ceramic ball on the top of the stem that acts as the new head of the femur.
Then the acetabulum (socket) of the hip joint is removed and replaced with a new metal socket. A spacer is placed between these two parts that can be metal, plastic, or ceramic to decrease friction within the hip joint
Anterior approach
With this type of hip replacement surgery the surgeon makes an incision on the front part of the upper thigh, and many times there is no need to cut through muscle. The removal of the damaged joint and then the addition of the implants is similar to the posterior approach.
This approach may allow for an earlier return to activities and a significant decrease in the risk of dislocation, but it is also a more technically challenging surgery with higher risks of injury during surgery due to the position the patient must be in and the proximity of a large nerve near the area the incision should be performed.
Hip Resurfacing

This is one of the types of hip surgery. Hip resurfacing has been developed as a surgical alternative to total hip replacement.
The procedure consists of placing a metal cap over the femoral head while a fitting metal cup is placed in the acetabulum (socket). There is less bone removal with this procedure compared to hip replacement. Also, with hip resurfacing there is an easier revision of surgery and a reduced chance of hip dislocation. However, there is an increased chance of femoral neck fractures, aseptic loosening and metal wear.
Hip Arthroscopy
Hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat problems of the hip joint and surrounding soft tissues. Hip arthroscopy is same-day surgery and is generally performed under general anesthesia. Hip arthroscopy usually takes between 1.5 to 2 hours, although the length of time can vary depending on the type of procedure being performed.
Hip arthroscopy comes in handy in the treatment of hip conditions such as labral tears, hip impingement, hip washout, chondral lesions, sciatic nerve compression, etc.
Hip arthroscopy has gained popularity because of the small incisions used and shorter recovery times when compared with conventional surgical techniques.
Hip Osteotomy
The procedure involves cutting and removing bone or adding a wedge of bone near a damaged joint. In the knee, for example, an osteotomy shifts weight from an area damaged by arthritis to an undamaged area. In the hip, it is often used to correct misalignment (hip dysplasia) that occurs early in life.
This operation is complex and is usually performed in specialized centers that do this procedure frequently. After the operation, patients should not put full weight on their leg for up to three months, so crutches or walkers are often recommended along with a wheelchair for longer distances until the bone has healed in its new position.
In conclusion, there are various types of hip surgery and they are performed based on a number of factors including, medical conditions, costs, patient and doctors preferences.


