Spinal Fusion Surgery | Indications | Cost | Technique
Overview
Low back pain remains one of the most expensive and difficult to treat chronic medical disease, with an estimated lifetime prevalence of 80 percent in adults and a yearly occurrence of 15 to 20 percent in the USA.
Back pain is the most prevalent complaint that necessitates a doctor’s assessment, accounting for 35 to 80 percent of workman’s compensation claims, second only to upper respiratory tract infections as a cause of work absence.
Despite inconsistent proof for considerable pain alleviation or improved patient outcomes, the use of lumbar spine fusion surgery to manage persistent back pain is on the rise amongst Eligible individuals.
What is Spinal Fusion Surgery
Spinal fusion surgery, also known as spondylodesis or spondylosyndesis, is a surgical union of vertebral bones to prevent vertebral instability.
With each procedure done, two or more vertebrae are fused and the involved segment becomes a single immobilized vertebra.
Sometimes during spinal fusion surgery, surgeons may insert additional bone to increase the sealing between the two adjacent vertebrae.
Types of Spinal Fusion Surgery
There are various types of spinal fusion Surgery and include the following:
Posterior interbody fusion
In this type, the patient is positioned in the prone (on his belly) position, and the intervertebral area is introduced through dissection of spinal muscles in the posterior direction.
Transforaminal interbody fusion
This type involves the unilateral entry to intervertebral foramina without the dissection of spinal muscles and disrupting the structural integrity. This type is proposed to avoid the excessive neural traction caused by posterior interbody fusion.
Anterior interbody fusion
The patient is positioned in the supine (on the back) position and provides total access to the anterior surface of the involved disc.
Lateral interbody fusion
This type allows good access to the lateral surface of the involved disc through the lateral retroperitoneal approach.
Oblique lateral interbody fusion
It involves gaining access to the disc space through the corridor between peritoneal coverage and psoas muscle.
Indications of Spinal Fusion Surgery
The following are the most common indication of this procedure:
Mechanical back pain. it is usually caused by disc degeneration (degenerative disc disease)
Spinal stenosis. It is a pathological narrowing of the spinal cord canal.
Isthmic spondylolisthesis. It is a disease in which one vertebra is sliding in the front of the vertebra below.
Fractures
Tumors Including benign and malignant tumors.
Contraindications of Spinal Fusion Surgery
There are few contraindications of spinal fusion surgery, mostly with the anterior approach, including:
• Previous abdominal surgery with adhesions
• Abnormal vascular structure
• Significant peripheral vascular disease
• Single kidney on the side of exposure
• Spinal infection
• Advanced degenerative spondylolisthesis
Equipment of Spinal Fusion Surgery
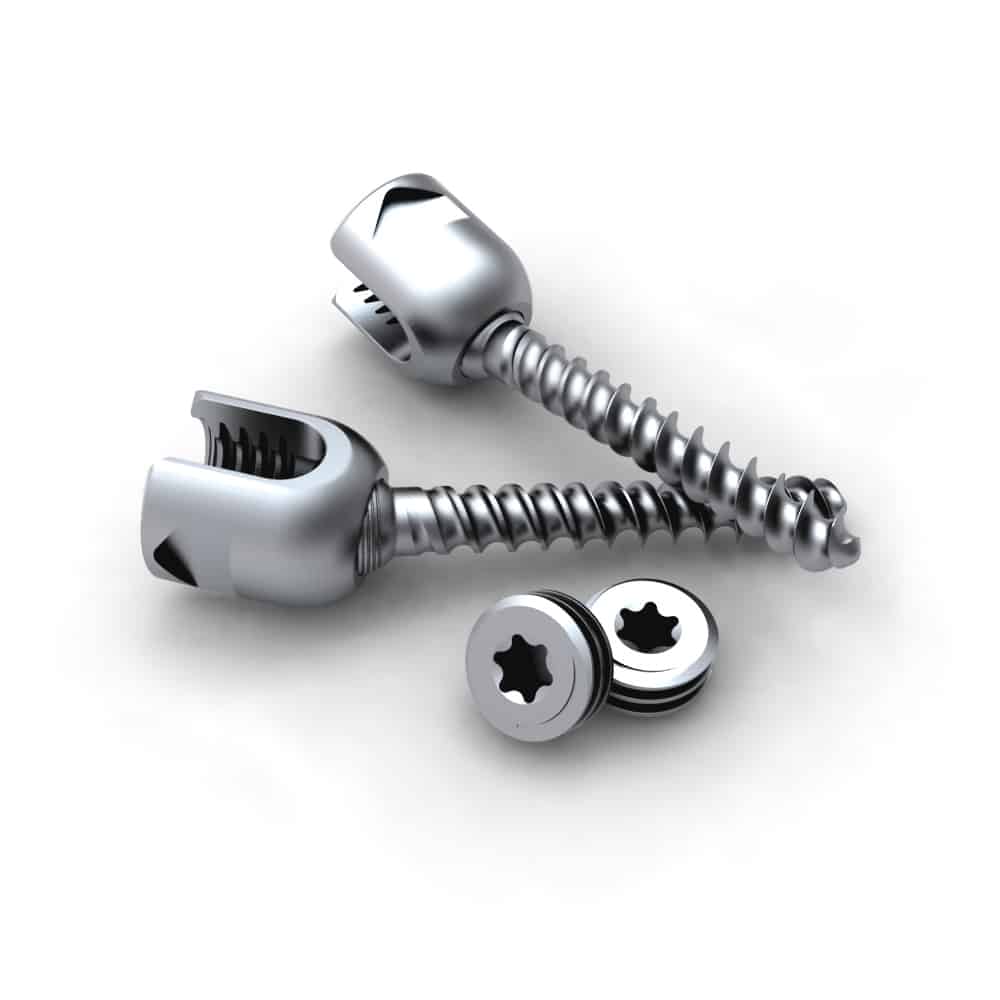

Spinal Fusion Surgery
The procedure is simple and requires a few surgical instruments including:
- Rods
- Plates
- Pedicle screws
- Anterior and posterior interbody cages
- Hooks
How Spinal Fusion Surgery is Done?
The following are the steps of spinal fusion surgery:
Making an incision
The doctor will make an incision on your back under ultrasound or CT guidance to plan the approach.
Locating the affected segment
The surgeon will enter the space and find the damaged disc to treat it. The blood vessels that run above and around the injured disc are carefully shifted and kept in place.
Removal of the discs
The injured disc is removed. The number of discs resected is determined according to how many segments of the spine are damaged. To open the compressed disc space, a distractor tool is introduced.
Preparation of the disk space
Spacer size is chosen after measuring the open disc space. The open disc space is put into the testing spacer.
Imaging is obtained to check that the depth and location are adequate to release the nerves and provide enough elevation.
After the fit spacer production, the bone graft is prepared to be fused.
Insertion of the bone graft
The spacer graft is placed in the open disc space under imaging guidance to press the two bones apart and maintain proper disc height.
Risks of Spinal Fusion Surgery
There are a few possible postoperative complications that include the following:
Postoperative infection To reduce the risk of infection, antibiotics are administered to patients before and after the operation.
Hemorrhage A tiny quantity of bleeding is to be anticipated, but it is rarely severe. Before a spinal fusion, it is typically not essential to give blood.
Continuous pain A small subset of patients will have ongoing pain at the location of the graft material.
Recurrence of initial symptoms It’s possible that some people will experience a repeat of their initial symptoms.
Nerves and blood vessels injury It’s probable that nerves or blood vessels will be damaged as a result of these procedures.
Blood clots The production of thrombosis in the legs is another unusual consequence.
How Long Does Spinal Fusion Surgery Last?
The surgery lasts on average between 3 to 7 hours to be completed with a postoperative hospital stay for 1 to 2 days.
Cost of Spinal Fusion Surgery
In the USA, Spinal fusion, which is often performed to repair issues such as a displaced vertebra, ruptured disk, or other spinal abnormalities, costs approximately 70,000$ to 130,000$.
See Also
References
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1343720-overview
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28327997/
https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/spinal-fusion/about/pac-20384523

Dr.Sharif Samir Alijla, is a general medical doctor and a well-rounded professional that cares and treats patients from Palestine. I participated in many medical studies and conferences, I've launched a range of community initiatives and taken part in a variety of leadership and change training programs. I worked as an author for many medical websites such as TebFact . I specialized in writing medical articles from authoritative and updated sources in a simple and smooth the way for the reader.