Photorefractive Keratectomy Surgery Overview
Photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) is a type of laser eye surgery used to improve vision by correcting refractive errors in the eye.
Examples of refractive errors of the eyes that can be corrected with PRK are nearsightedness, farsightedness and astigmatism.
Nearsightedness (myopia) is a condition in which close objects appear clearly, but far ones don’t. Faraway objects appear blurry. The condition may develop gradually or rapidly. The condition is often due to genetics.
Farsightedness (hyperopia) is the opposite of nearsightedness. In this condition, nearby objects are blurry. Hyperopia is a common vision condition in adults.
People with hyperopia must squint to see nearby objects. Reading, writing, computer work or drawing for long periods of time may cause eye strain and headache.
With astigmatism, the front surface of the eye or the lens inside the eye is curved differently in one direction than the other. A common symptom is a blurry vision.
PSK surgery helps to reduce or totally eliminate the need for glasses or contact lenses.
An alternative to PRK surgery is LASIK surgery. PRK predates LASIK surgery and is a similar procedure.
Both PRK and LASIK work by reshaping the cornea, which is the clear front part of the eye. This improves the eye’s ability to focus.
Some people are good candidates for both PRK and LASIK. Others are better suited to one or the other.
More: Types of Cataract Surgery
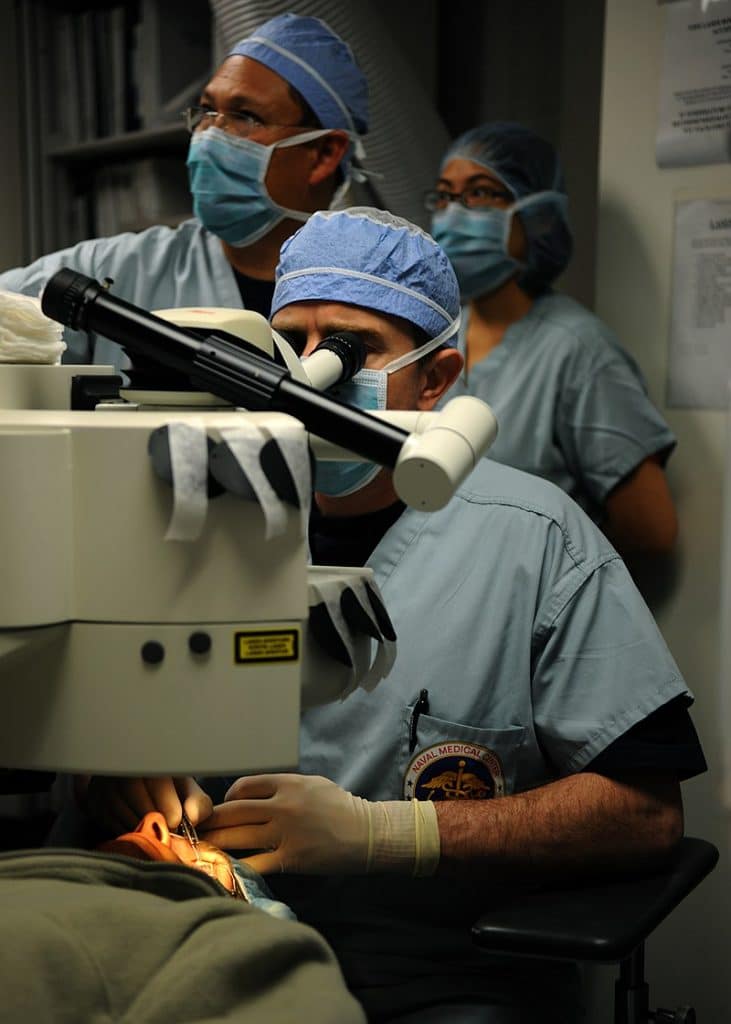
PRK procedure
PRK takes 5 to 10 minutes per eye and is usually performed under local anesthesia given as eye drops.
During the procedure:
– An eyelid holder will be placed on each eye to prevent blinking.
– The surgeon will remove and discard the corneal surface cells of the eye. This may be done with a laser, blade, alcohol solution, or brush.
– The laser that was programmed with the eyes’ measurements will reshape each cornea, using a pulsing beam of ultraviolet light.
– A clear, nonprescription contact lens will be placed on each eye as a bandage. This will keep the eyes clean, avoiding infection during the healing process. The bandage contact lenses will remain on the eyes for several days to one week.
PRK Risks and Complications
Like all surgical procedures, PRK has its own risk of complications. Some complications that can be temporary or permanent include:
- Dry eyes
- Recurrent erosions during sleep
- Long healing period
- Pain
- Glare, halos, or starburst aberrations
- Increased ocular straylight
- Under- or overcorrection
- Recurrence of myopia
- Corneal haze
- Scarring
- Reduced best-corrected visual acuity
- Reduced acuity in low light
- Increased sensitivity
Advantages of PRK
- An estimated 90 to 95 percent of people who undergo PRK achieve 20/40 vision or better without wearing glasses or contacts. You may still need glasses for reading and nighttime activities, and vision typically declines with age.
- PRK can achieve the same long-term benefits as LASIK.
- PRK may be an alternative option for people who are not good candidates for LASIK, including patients with thin corneas.
- Athletes may be better candidates for PRK rather than LASIK. During LASIK, a flap is cut into the cornea and can be dislocated by strenuous activity during recovery.
Disadvantages of PRK
- Any surgery comes with risks. Complications of PRK may include scarring, infection, cloudiness of the cornea, and a “halo effect” around lights.
- There is a risk of over or under correction of your vision—this is often remedied with glasses, contacts, or additional surgery.
- In rare cases, vision may become worse after PRK.
- Initial recovery time is longer LASIK. Many people notice better vision within days of PRK, but it can take several days for the epithelium to heal and up to three months for vision to stabilize.
PRK Surgery Cost
The total cost for PRK surgery depends on a lot of factors such as the anesthetic fee, private hospital fee, private operating facility fee, the extent of surgery required. The total cost of the procedure is around $1500 – $4000.