Mesothelioma refers to cancer of the mesothelium, the thin layer of tissue that covers the majority of the internal organs.
Mesothelioma is an aggressive and deadly form of cancer with. Mesothelioma treatments are available, but for many people with mesothelioma, a cure isn’t possible.
There are different types of mesothelioma depending on the location of the cancer including:
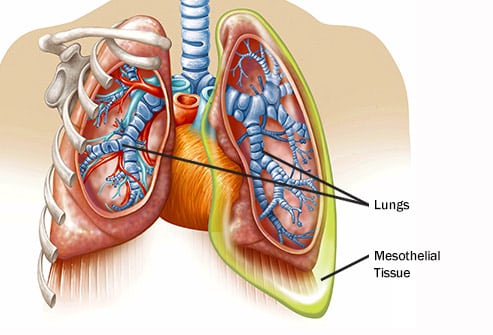
Pleural mesothelioma: This type of mesothelioma affects the pleural, i.e the tissue that surrounds the lungs and chest walls. The signs and symptoms of pleural mesothelioma are:
– Chest wall pain
– Pleural effusion, or fluid surrounding the lung
– Shortness of breath – which could be due to a collapsed lung
– Fatigue or anemia
– Wheezing, hoarseness, or a cough
– Blood in the sputum (fluid) coughed up (hemoptysis)
More: Surgery For Lung Cancer
Peritoneal mesothelioma: This type occurs in tissue in the abdomen. Signs and symptoms may include:
– Abdominal pain
– Abdominal swelling
– Nausea
– Unexplained weight loss
Other rare forms of mesothelioma affects the tissues surrounding the heart and testis.
More than 80% of mesothelioma cases are caused by exposure to asbestos. The greater the exposure the greater the risk
Mesothelioma Treatment
Mesothelioma treatments are available, but for many people with mesothelioma, a cure isn’t possible. The earlier the cancer is diagnosed, the better the outcome of treatment. Mesothelioma treatment options are namely:
- Surgery
- Radiotherapy
- Chemotherapy
1. Mesothelioma Surgery
Patients diagnosed in the early stages benefit most from mesothelioma surgery. It offers them the best chance at living longer lives. These procedures, often performed with chemotherapy, remove all visible tumors from the chest area and improve quality of life.
There are different surgical options to treat mesothelioma depending on the goal of the procedure and the stage of the cancer. These surgical options are:
a. Diagnostic Mesothelioma Surgery
This is a type of surgery performed to diagnose the stage of the cancer. Doctors may recommend a biopsy to diagnose malignant mesothelioma. A biopsy is the removal of a fluid or tissue sample for analysis. It is the only way to definitively confirm a diagnosis of mesothelioma.
Biopsies can be minimally invasive. However, some are considered open surgical procedures because the impacted tissue or fluid may be more difficult to reach.
b. Mesothelioma Cytoreductive Surgery
This surgery is performed to reduce the number of cancerous cells in the body. For best results, it is often performed in combination with other treatments such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy in which the treatment plan is known as multimodality therapy.
This aggressive treatment approach can extend life expectancy and potentially send mesothelioma into remission. Remission isn’t a cure, but it provides time for patients to live without having to cope with active cancer in their body.
c. Palliative Surgery
Palliative surgery is surgical intervention targeted to make a patient’s symptoms less severe, thus make the patient’s quality of life better despite negligible impact on the patient’s survival. Palliative surgery focuses on supplying the greatest benefit to the patient using the least invasive intervention. Palliative surgery provides symptom relief and preservation of the quality of life in terminal disease states.
2. Radiotherapy
For patients with localized disease, and who can tolerate a radical surgery, radiation can be given post-operatively as a consolidative treatment. The entire hemithorax is treated with radiation therapy, often given simultaneously with chemotherapy. Delivering radiation therapy and chemotherapy after a radical surgery has led to extended life expectancy in selected patient populations. It can also induce severe side-effects, including fatal pneumonitis. As part of a curative approach to mesothelioma, radiotherapy is commonly applied to the sites of chest drain insertion, in order to prevent growth of the tumor along the track in the chest wall.
Although mesothelioma is generally resistant to curative treatment with radiotherapy alone, palliative treatment regimens are sometimes used to relieve symptoms arising from tumor growth, such as obstruction of a major blood vessel. Radiation therapy, when given alone with curative intent, has never been shown to improve survival from mesothelioma. The necessary radiation dose to treat mesothelioma that has not been surgically removed would be beyond human tolerance.[citation needed] Radiotherapy is of some use in pericardial mesothelioma.
3. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy also known simply as chemo is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen.
Chemotherapy is the only treatment for mesothelioma that has been proven to improve survival in randomised and controlled trials.
There are two methods of administering chemotherapy: systemic chemotherapy or intracavitary chemotherapy.
In systemic chemotherapy, drugs are administered through an IV (intravenously), by injection or pill form. The chemotherapy drugs reach any part of the body where blood flows. As a result, fast-growing cells, such as cells in hair follicles and healthy blood cells, may die along with cancer cells.
With intracavitary chemotherapy, drugs are administered during surgery into areas where the tumors have formed.
Chemo drugs used for mesothelioma treatment include Pemetrexed, Cisplatin, Carboplatin, Vinorelbine, etc.
More: Hair Transplant Surgery
4. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that helps your immune system fight cancer. The body’s disease-fighting immune system may not attack your cancer because the cancer cells produce proteins that blind the immune system cells. Immunotherapy works by interfering with that process. This treatment might be an option if other treatments aren’t working.
Prognosis
Mesothelioma often has a poor prognosis. Typical survival despite surgery is between 12 and 24 months depending on the stage of disease at diagnosis with about 8% of people surviving for 5 years.
Women, young people, people with low-stage cancers, and people with epithelioid cancers have better prognoses. Factors that affects prognosis negatively include age over 50 years, sarcomatoid or biphasic histology, high platelet counts, high white blood cell counts, low glucose levels in the pleural fluid and low albumin levels. Long-term survival is rare.
More: Mohs Surgery