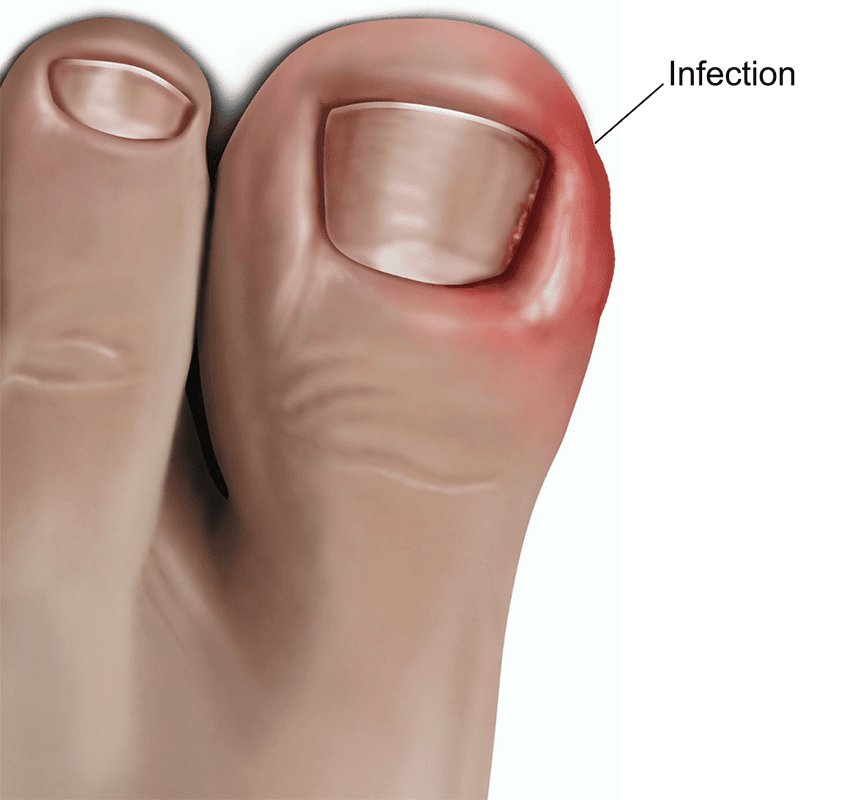
An ingrown nail is a nail condition in which the nail grows so that it cuts into one or both sides of the nail bed. Ingrown nail often results in pain, redness, swelling and sometimes, an infection.
Ingrown nail occur most commonly on the toenails (ingrown toenail) and mostly problematic and painful on the bigtoe. Causes of ingrown toenail include ill-fitting shoes, genetics, trauma and disease. The condition is treated conservatively and if need be surgically.
More: Capsulotomy
Ingrown Nail Signs and Symptoms
Ingrown toenails can be painful, and they usually worsen in stages.
Early-stage symptoms include:
- skin next to the nail becoming tender, swollen, or hard
- pain when pressure is placed on the toe
- fluid building up around the toe
If the toe becomes infected, symptoms may include:
- red, swollen skin
- pain
- bleeding
- oozing pus
- overgrowth of skin around the toe
The earlier an ingrown nail is treated the better the prognosis.
Ingrown Nail Treatment
The treatment of an ingrown toenail partly depends on its severity.
Conservative treatment
Mild to moderate cases are often treated conservatively with warm water and epsom salt soaks, antibacterial ointment and the use of dental floss. If conservative treatment of a minor ingrown toenail does not succeed, or if the ingrown toenail is severe, surgical treatment may be required.
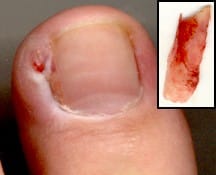
Ingrown Nail Surgery
Surgical treatment of ingrown nail is indicated when conservative means have proved abortive. Surgical treatment for an ingrown nail is carried out by a podiatrist, a foot and ankle specialist. This is typically an in-office procedure requiring local anesthesia and special surgical instruments. The surgical approach is the removal of the offending part of the nail plate known as a wedge resection. If the ingrown toenail recurs despite this treatment, destruction of the sides of the nail with chemicals or excision is done; this is known as a matrixcestomy
There are different types of surgical treatments for ingrown nails.
i. Wedge resection
The physician will perform an onychectomy in which the nail along the edge that is growing into the skin is cut away (ablated) and the offending piece of nail is pulled out and any infection is drained. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and takes is about forty-five (45) minutes.
A wide wedge resection, with a total removal of nail matrix, has a nearly 100% success rate.
ii. Avulsion / Toenail removal
A doctor may decide to remove the entire toenail. Removing the whole nail makes it more likely that the nail will grow back misshapen or deformed, which can increase the risk of future ingrown toenails. It can take up to 18 months for the nail to regrow fully which could be more problematic if it became ingrown again. As a result, as determined by the doctor, the nail matrix is coated with a chemical (usually phenol) so none of the nail will ever grow back. This is known as a permanent or full nail avulsion.
iii. Syme procedure
In difficult or recurrent cases of ingrown nail the patient’s symptoms persist necessitating a permanent operative solution. The “avulsion procedure” is simple but the surgeon must be skilled enough to accomplish total destruction, and removal of, the nail matrix. Another disadvantage is the long healing and recovery time(> 2 months). In these cases, the best method is the Syme procedure, that means total nail matrix removal + skin flap transfer + phalanx partial osteotomy + stitching.
Ingrown Nail Surgery Cost
The total cost for ingrown toenail surgery depends on a lot of factors such as the anesthetic fee, private hospital fee, private operating facility fee, extent of surgery required. The total cost of the procedure is around $250 – $300.
Recovery
The patient is allowed to go home the same day and the recovery time is anywhere from two weeks to two months barring any complications such as infection. As a follow-up, a physician may prescribe an oral or topical antibiotic or a special soak to be used for about a week after the surgery.
More: Rib Removal Surgery