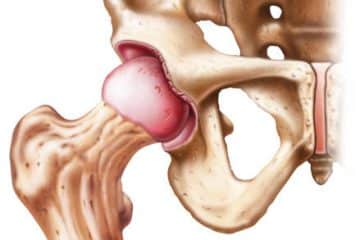
Hip Replacement Surgery – Overview
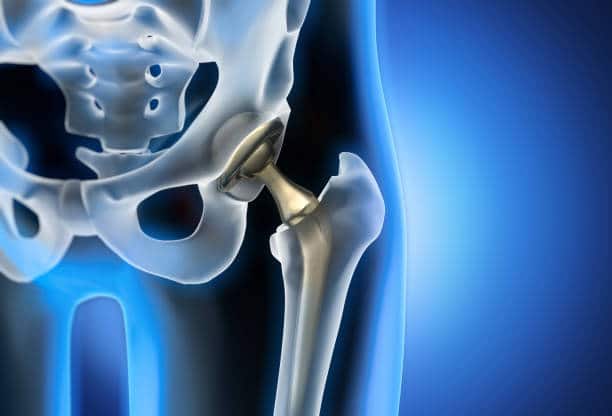
Hip Replacement Surgery
Total hip replacement surgery (total hip arthroplasty) is an excellent therapy option for patients with severe end-stage degenerative hip joint disease. It helps relieve pain, restore mobility, and improve functionality.
Total hip replacement is performed on roughly 35 percent of patients below the age of 55, and this number is continuously rising.
It is one of the most popular orthopedic procedures. its effectiveness in elderly patients, combined with advancements in the methods and used components, has sparked interest in the operation among younger people.
What is Hip Replacement Surgery?
Hip replacement surgery, also known as hip arthroplasty, is a surgical intervention for treating hip pain and other related diseases.
Synthetic prostheses are used to substitute components of the hip joint. The hip joint composes of the head of the femur (thigh bone) and the hollow content of the hip joint (part of the pelvic bone).
One or both portions of the hip are replaced during hip replacement surgery. The procedure’s objective is to help you return to regular daily activities with much less pain.
Types of Hip Replacement Surgery
There are two types of hip replacement and include:
• Total hip replacement. In which both the head and socket of the hip joint are replaced.
• Partial hip replacement. In which either the head or socket of the hip joint is replaced.
Indications of Hip Replacement Surgery
The following are indications for hip replacement surgery:
- Arthritic including Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis, and traumatic arthritis.
- Hip dysplasia (congenital diseases affecting the hip joint)
- Severe pain that doesn’t respond to nonsurgical treatments (e.g., analgesics).
- Limitations on daily activities.
- You can’t get to sleep because of your suffering.
- Mobility is limited due to hip discomfort.
Contraindications of Hip Replacement Surgery
Absolute Contraindications
- Patient having a serious medical condition that increases the mortality risk.
- An infection or sepsis in the hip joint.
- Bacteremia or active infection elsewhere in the body.
Relative Contraindications
- Any condition that causes rapid destruction of the joint.
- Neuropathic joint disease
- Widespread progressive osteopenia.
- Abductor muscles weakness.
- Worsening neurological diseases
Equipment of Hip Replacement Surgery
Hip Replacement Surgery – Equipment
The hip replacement kit involves the following items:
- Cement Removal instruments
- Curettes
- Elevators
- Forceps
- Hooks
- Orthopedic Pliers
- Osteotomes and Rasps
- Self-Retaining Retractors
- Hand-held retractors
- Rongeurs
- Spreaders
See Also: List of Surgical Instruments
How Hip Replacement Surgery is Performed?
The operation is usually done under general anesthesia.
There are different approaches to perform knee replacement:
- Posterior (Southern)
- Direct anterior (Smith-Petersen)
- Anterolateral (Watson-Jones)
- Direct lateral (Hardinge)
The following are the steps of knee replacement:
Making an Incision
To uncover the bones at the hip joint, the doctor creates an incision on the lateral or behind the hip joint, cutting through skin, muscle, and other soft tissue.
A small incision in the front of the hip during anterior hip replacement.
Removal of Femoral Head
The joint is dislocated, and the head of the femur is removed from its socket in the pelvis. The acetabulum is the name for this socket.
A bone cutter is used to remove the arthritic femoral head. The surgeon grinds down and shapes the acetabulum in preparation for the acetabular cup implant with a hemispheric reamer.
Insertion of Acetabular Liner and Femoral Stem
Inside the acetabular cup, the surgeon inserts a spherical acetabular liner. The liner, which might be made of porcelain or plastic, will allow for easy motion in the new prosthetic joint.
The doctor trims the femur bone before implanting the artificial femoral stem. The femoral stem is a thin, curved metallic shaft that extends many centimeters into the femur. The stem’s tip is made to hold an artificial sphere that will substitute the femoral head.
Risks of Hip Replacement Surgery
The following are possible complications after hip replacement surgery:
Prosthetic dislocation It is associated more with the direct lateral approach than with the posterior approach.
Periprosthetic fracture The incidence of these fractures is becoming more common as the number of surgeries performed on younger patients increases.
Prosthesis aseptic loosening It involves debris formation and prosthesis micromovement, and if there is persistent pain the patient should undergo revision surgery.
Wound risks It includes various problems such as cellulitis, dehiscence, delayed wound healing, and deep-tissue necrosis.
Prosthetic joint infection Following primary total hip replacement, about 1 to 2 percent of patients develop a prosthetic joint infection.
Venous thromboembolic diseases They include life-threatening pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis (leg vein clots).
How Long Does Hip Replacement Surgery Last?
This operation requires 1-2 hours to be completed and the patient should stay in the hospital for 1-2 days under observation.
Cost of Hip Replacement Surgery
According to different hospitals, the average cost of hip replacement surgery is approximately 20,000$ to 30,000$.
See Also
References
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4358426/
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/546103
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2000333-overview
https://www.physio-pedia.com/Total_Hip_Replacement

Dr.Sharif Samir Alijla, is a general medical doctor and a well-rounded professional that cares and treats patients from Palestine. I participated in many medical studies and conferences, I've launched a range of community initiatives and taken part in a variety of leadership and change training programs. I worked as an author for many medical websites such as TebFact . I specialized in writing medical articles from authoritative and updated sources in a simple and smooth the way for the reader.