Hip Joint Surgery
Overview

Hip Joint Surgery
Hip replacement surgery (Hip arthroplasty) is a remarkably effective procedure in which implants are used to replace parts of the hip joint (prostheses).
Hip arthroplasty is regarded as a highly successful procedure with consistent results. The artificial hip works similarly to a natural hip and improves a person’s quality of living greatly.
Current prosthetic hip joints are built to last for at minimum two decades. The majority of people report a considerable reduction in discomfort and an increase in joint movement.
Another procedure of the hip joint that is less common than hip replacement surgery is hip joint osteotomy.
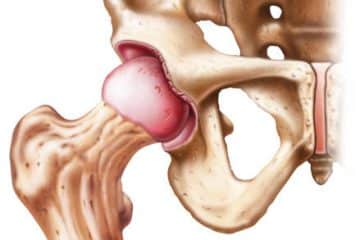
Hip Joint Anatomy
The hip is among the most important axial joints in the body, comprising two main components:
A spherical cavity (acetabulum) in your pelvis and a globe (femur head) at the top of the femur bone (thighbone).
Ligaments connect the ball to the socket and help to keep both portions of the hip stable. Ligaments are strands of robust yet elastic tissue. The ball and socket are cushioned by fibrocartilage, a small layer of lubricant tissue that allows the hip joint to move freely.
A thin layer of smooth fibrous tissue called synovial membranes covers the other surfaces of the hip joint, producing a tiny quantity of viscous fluid to prevent the bones from rubbing against each other.
Types of Hip Joint Surgery
• Total hip joint replacement
• Partial hip joint replacement
• Hip joint resurfacing
• Hip joint osteotomy
Indications of Hip Joint Replacement Surgery
Arthritis is the most common source of chronic hip aches and impairment.
The most frequent types of arthritis include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-trauma arthritis.
• Osteoarthritis. This is a type of arthritis that develops with aging. It mainly affects adults over the age of 60, and it’s much more common in persons who have a family history of osteoarthritis. The cartilage that cushions the hips breaks away. Hip pain and stiffness resulting from the bones rubbing against each other. Osteoarthritis can also be triggered or hastened by minor flaws in how the hip grew as a child.
• Rheumatoid arthritis. it is a kind of arthritis that attacks the joints. The synovial membrane becomes irritated and inflamed in this autoimmune disorder. Persistent and prolonged inflammation can cause cartilage degradation, resulting in pain and rigidity. Rheumatoid arthritis is by far the most frequent kind of inflammatory arthritis.
• Traumatic arthritis. This may occur as a result of a major hip injury or fracture. With ages, the cartilage may be destroyed, resulting in hip discomfort and rigidity.
• Hip disease in childhood. Hip disorders affect certain newborns and youngsters. Even if the disorders are properly managed throughout childhood, arthritis can develop later in life. This occurs also because hip may well not develop correctly, causing damage to the joint surfaces.
Equipment of Hip Joint Surgery
Following surgical equipment are being used during hip joint surgery
- Rongeur
- Charnley type self-retaining retractor
- Tissue forceps
- Orthopedic drill
- Hohmann retractor
- Sterile marker
- Acetabular retractor
- Orthopedic mallet
- Reduction forceps
- Orthopedic chisel and osteotome (used in hip joint osteotomy)
Total Hip Joint Replacement Surgery
The diseased bone and cartilage are removed and replaced with prosthetic components in a total hip replacement (also referred to as total hip arthroplasty).
The injured femoral head is excised, and a metallic shaft is inserted into the internal middle of the femoral shaft to replace it. In the bone, the femoral shaft can be cemented or pressed in.
On the upper half of the stem, a hardened steel sphere is put. This sphere replaces the femoral head that was lost due to injury.
The acetabulum injured cartilaginous surface is abolished and replaced with a metallic implant. The socket is occasionally held in place with nails or cement.
A smooth gliding surface is achieved by inserting a plastics, porcelain, or metallic cushion between the implanted ball and the socket.
Partial Hip Joint Replacement Surgery
Partial hip replacement is a procedure that entails replacing the fractured femoral head, cutting the broken end of the neck, and implanting a femoral shaft. The femoral shaft is cemented or non-cemented and is implanted similarly to a total hip replacement. The acetabulum isn’t really harmed because it is still in excellent condition.
Hip Joint Resurfacing Surgery
The femoral head is not excised during hip resurfacing; instead, it is clipped and covered with a low-friction metallic coating. As with standard total hip arthroplasty, the injured bone and cartilage within the joint cavity is scrapped and replaced with a metallic casing.
Hip Joint Osteotomy Surgery
Femoral osteotomy is a surgical intervention used to address abnormalities of the femur and hip joint. The operation, which includes cutting the bone, is performed by orthopedic surgeons in an attempt to straighten it and reestablish a more normal structure, thereby resolving or avoiding complications associated with the deformity. Articular cartilage degradation in the hip joint breaches in the labrum (the crescent-shaped elastic component that extends around the edge of the hip socket), and other forms of hip bone disordered contact, are all possible causes of hip malalignment.
Specific indications of hip osteotomy
• Developmental dysplasia of the hip.
• Perthes’ disease.
• Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE).
• Osteonecrosis.
• Congenital deformity.
References
https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/treatment/total-hip-replacement/
https://www.hss.edu/condition-list_hip-replacement.asp
https://www.verywellhealth.com/considering-hip-replacement-surgery-2549565
See Also
Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome

Dr.Sharif Samir Alijla, is a general medical doctor and a well-rounded professional that cares and treats patients from Palestine. I participated in many medical studies and conferences, I've launched a range of community initiatives and taken part in a variety of leadership and change training programs. I worked as an author for many medical websites such as TebFact . I specialized in writing medical articles from authoritative and updated sources in a simple and smooth the way for the reader.