BMI for Weight Loss Surgery
According to WHO worldwide obesity has tripled since 1975 and in 2016 nearly 2 billion adults (39% of adults aged 18 years and over) were overweight. Out of 2 billion adults, 650 million (13% of adults) were obese.
Severe obesity is a chronic condition associated with numerous health problems. Unfortunately, in lots of cases, diet and exercise alone are not sufficient to regain control of body weight.
Gastric bypass and other surgical weight loss procedures, collectively known as bariatric surgery, often serve as the last resort for severely obese patients. But not everyone, suffering from excess weight, becomes a candidate for these procedures since one needs to meet certain Body Mass Index (BMI) criteria.
In the article below we will discuss how BMI values determine a patient’s eligibility for bariatric surgery and what other factors need to be taken into account.
Understanding your BMI Results
Body mass index is one of the most popular indicators for determining the degree of obesity. With the help of BMI, the correspondence of body weight to height is determined.
BMI is obtained by dividing body weight in kilograms by the square of body length (in meters). For example, a man who is 1.80 m tall and weighs 80 kg will have a BMI 80 / (1.80)² = 24.69.
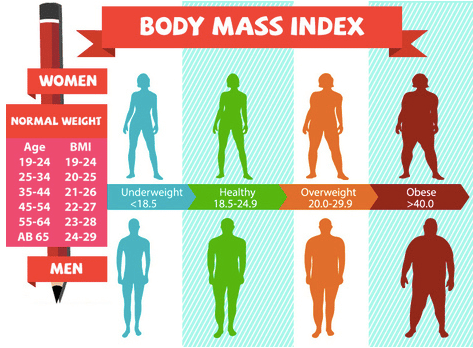
Results are interpreted as follows:
BMI under 18.5 – underweight
18.5 – 24.9 – normal weight
25 – 29.9 – overweight
30.0 – 39.9 – obese
BMI over 40 – morbidly obese
Keep in mind that such interpretation of BMI values does not apply to children and elderly, and adults with high muscle mass. Special growth charts are used to evaluate the weight of children and adolescents.
In the elderly generally higher than normal BMI is considered normal. And in the case of muscular adults, BMI values will not depict their fitness, since muscle weighs much more than fat.
BMI for Weight Loss Surgery
Who is a Candidate for Bariatric Surgery?
In general, people with a BMI of 40 or higher are eligible for bariatric surgery and will get insurance coverage.
Apart from that, weight loss surgery can be an option for adults with BMI between 35 and 40, in case they have any obesity-related disease or have a documented history of unsuccessful weight-loss attempts.
The latter requirement should not come as a surprise, since bariatric surgery is a major surgical procedure and poses potential health risks.
Hence doctors must be completely sure that non-surgical measures alone are insufficient. On the other hand, a BMI of 50 or more usually grants weight loss surgery without the need to try alternative methods first.
We have already mentioned that BMI interpretation is not directly applied to children and adolescents, but according to guidelines the adolescents who have reached their adult height (usually 13yrs or older for girls and 15 or older for boys) and have BMI >40 + obesity-associated medical condition or BMI >35 + severe obesity-related medical condition, may benefit from surgical intervention.
High blood pressure, pulmonary hypertension, type 2 diabetes, various types of heart diseases, sleep apnea, varicose veins, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, etc – all of the following medical conditions are caused or at least aggravated by excess body weight.
Any of these plus BMI >35 makes a person a candidate for bariatric surgery.
Weight Loss Surgery Procedures
Bariatric surgery refers to surgical intervention in the digestive tract to achieve significant and permanent weight loss and to alleviate diseases associated with obesity (eg, type II diabetes, high cholesterol). Surgery reduces the volume of the stomach or shortens the portion of the small intestine where ingested food passes.
The goal is the same in both cases: limiting food intake and absorption. After the operation, patients begin to feel full after smaller portions, thus it’s substantially easier to alter their eating habits and dietary patterns.
As a result, the patient’s BMI is reduced in the long run, and life expectancy increases.
In the U.S the most common weight-loss surgery types are adjustable gastric band, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, biliopancreatic diversion with a duodenal switch, and vertical sleeve gastrectomy.
Factors Other Than BMI Affecting Weight Loss Surgery
To qualify for bariatric surgery, excess weight and medical issues are not enough. Patients must express their willingness to stick to a further pre-surgery preparation and post-surgery treatment plan that includes menu planning, exercise schedule, smoking cessation, and psychotherapy as well since extreme obesity is sometimes linked to eating disorders.
The risks associated with a major surgery should also be assessed. Many of the above-listed obesity-associated conditions significantly increase the risk of anesthesia and post-surgery complications.
Summary
Adults with BMI >40 or with BMI> 35 plus any obesity-associated health issue are candidates for weight loss surgery. They will also have to commit to healthy eating and regular exercise. These habits reduce the risk of further weight gain and let patients enjoy surgery effects.
References: