Eye muscle surgery is a surgical procedure that is performed on the extraocular muscles to correct strabismus. The procedure is also known as strabismus surgery, extraocular muscle surgery, or eye alignment surgery.
In the United States, approximately 1.2 million procedures are performed each year making it the third most common eye surgery just behind cataract extraction and glaucoma surgery.
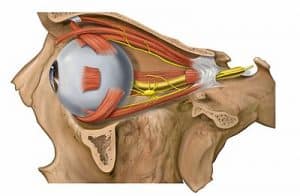
The extraocular muscles are made up of six muscles that control the movement of the eye and one muscle that controls eyelid elevation.
The six extraocular muscles are namely; Medial Rectus, Lateral Rectus, Superior Rectus, Inferior rectus, Superior oblique and Inferior oblique muscle. The muscle responsible for eyelid elevation is the Levator palpebrae.
eye muscle surgery
Strabismus is a condition in which the eyes do not align properly with each other when looking at an object. Strabismus can occur due to muscle dysfunction of the extraocular muscles, hence, if a muscle is too strong compared to its complimentary muscle, it may cause the eye to turn in, turn out or rotate too high or low.
Types of Eye Muscle Surgery
Eye muscle surgery involves detaching and reattaching the muscles to another position on the eye.
There are various types of eye muscle surgery depending on the affected muscles and techniques used namely:
- Loosening/weakening procedures
- Tightening/strengthening procedures
- Transposition/repositioning procedures
- Adjustable suture surgery
Loosening/weakening procedures
These are procedures that are performed on the eye muscles to weaken the relative strength of the muscle. They include:
i. Recession – In a recession procedure, the eye surgeon detaches the affected extraocular muscle from the eye and reattaches it (resection) farther back on the eye to weaken the relative strength of the muscle if it is too strong.
ii. Myectomy – This is performed to remove part of the muscles responsible for elevation of the eyelid.
iii. Myotomy – This refers to cutting part of the affected eye muscle
iv. Tenectomy – This is the surgical resection of part of a tendon
Tightening/strengthening procedures
These are procedures used to strengthen an eye muscle to correct misalignment associated with strabismus. They include:
i. Resection – This involves detaching one of the eye muscles, removing a portion of the muscle from the distal end of the muscle and reattaching the muscle to the eye.
ii. Advancement – This is the movement of an eye muscle from its original place of attachment on the eyeball to a more forward position.
Transposition/repositioning procedures
Here, the mechanical properties of muscle action are modified such that the direction of movement of the eye following a contraction of the muscle is altered.
Adjustable suture surgery
With adjustable suture eye muscle surgery, the surgeon adjusts sutures holding eye muscles in place after a resection procedure, to attempt to improve your outcome.
In most cases, adjustable suture surgery is performed in the operating room, with general or local anesthesia. Afterward, the eye is patched. About four to 24 hours later, the patch is removed in the office, when anesthesia and sedation have faded. Ocular alignment is then evaluated.
Based on how your eyes are aligned, your surgeon may decide to use the suture that is in place to tighten or loosen the treated muscle. This adjustment may cause slight discomfort, primarily with muscle tightening.
Once the desired alignment is achieved, the surgeon ties the adjustable suture permanently in place, and the procedure is complete.
Eye Muscle Surgery Procedure
Strabismus surgery is carried out under general anesthesia for children while it can be performed under local or general anesthesia for adults. The duration of the surgery can range from 45 minutes to 2 hours depending on the type of eye muscle surgery.
After surgery, the patient should expect soreness and redness. The surgeon will provide the patient with a cover for his or her eyes that prevents light from entering. The patient should wear this since stimulus to the eye (e.g., light, rolling of eyes) will cause discomfort.
Eye Muscle Surgery Risks and Complications
Like every surgical procedure, strabismus surgery comes with its possible risks and complications. Some of the risks and complications following surgery are:
- Double vision – Also known as diplopia, is a possible complication and it occurs in the first few weeks post-operation
- Scarring – Strabismus surgery gives rise to scarring (fibrosis); if scarring is extensive, it may be seen as raised and red tissue on the white of the eye. Fibrosis can be reduced by the use of mitomycin C during surgery.
Other rare complications are eye infections, bleeding, loss of vision and oculocardiac reflex which can be life-threatening.
Eye Muscle Surgery Recovery
During the first few days after surgery, eye alignment is a good indicator of the outcome. However, more permanent results may not be known until four to six weeks after surgery.
Children younger than 10 will very likely need a second or third strabismus procedure to maintain the best possible eye alignment. In some cases, eyeglasses or special lenses (prisms) placed in a pair of glasses may help fine-tune the way both eyes work together
Eye Muscle Surgery Cost
The total cost for eye muscle surgery depends on a lot of factors such as the anesthetic fee, private hospital fee, private operating facility fee, the extent of surgery required. The total cost of the procedure is around $3000 – $5500.
Read More: History of Surgery