Knee Replacement Cost and Procedure
Overview
The replacement of the knee, also known as knee arthroplasty, is the repair or reconstruction of a damaged knee joint. It’s more frequently known as a total knee replacement, and it’s a fairly safe and straightforward treatment.
Patients with symptomatic multicompartmental osteoarthritis of the knee who’s already failed conservative treatment should consider total knee arthroplasty.
The main objective of this operation is to provide long-term pain management while also improving functional capacity.
What is Knee Replacement?
Knee Replacement Surgery Cost
Knee replacement is a surgery performed to relieve pain and impairment by replacing the surfaces of the hinged knee joint.
It is most typically used to treat osteoarthritis, although it can also be used to treat rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis when it is indicated.
Types of Knee Replacement
There are four designs of knee joint prostheses
1. Cruciate-retaining Prosthesis
For the cruciate-retaining prosthesis to give strength in bending, the posterior cruciate ligament must be healthy. As a result, it should not be used in individuals who have pre-existing or intra-operatively diagnosed posterior cruciate impairment.
Advantages
o Tibial impingement and instability are prevented.
o Theoretically, maintaining more regular architecture that mimics normal knee.
o Bone stock that has been preserved
o Posterior cruciate ligament kinesthetic awareness in its natural state
Disadvantages
o Earlier polyethylene degradation can be caused by a tight posterior cruciate ligament.
o A weak or torn posterior cruciate ligament causes flexion imbalance and the risk of displacement or dislocation.
2. Posterior-Stabilized Prosthesis
The posterior cruciate ligament must be sacrificed in the posterior-stabilized total knee replacement design, which is significantly more restricted.
Advantages
o Allows for greater knee flexion
o Allows the knee to be more balanced overall
o Lower axial rotation and condylar translation
Disadvantages
o Patellar clunk syndrome is a condition that affects the patellar tendon.
o Erosion or fracture of the tibial bone
3. Constrained Nonhinged Prosthesis
The constrained nonhinged prosthesis has a bigger tibial post and a wider femoral cage, which provides more stability and restraint in both the varus-valgus and internal-external rotatory planes.
In the context of neurological arthropathy, collateral ligament atrophy or insufficiency, flexion gap instability, and mild bone loss are this design is indicated.
4. Constrained Hinged Prosthesis
The femoral and tibial elements of the constrained hinged design are interconnected. The tibial component can rotate around a yoke in a rotating hinge, which potentially reduces the risk of aseptic slippage while improving prosthetic restraint.
Widespread ligamentous deficits, malignancy removal, and severe bone loss in the setting of a neuropathic joint are all indications.
Indications of Knee Replacement
The most common indication for knee replacement is arthritis including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and traumatic arthritis.
The doctor will recommend the surgery for you when:
• Knee discomfort or tightness that prevents you from doing daily activities.
• Moderate/Severe knee discomfort while relaxing throughout the day.
• Knee swelling and pain does not decrease with relaxation or treatment
• Apparent knee deformity.
• failure of conservative therapy to control the pain and improve the joint function
Contraindications of Knee Replacement
Absolute Contraindications
o Active infection of the knee
o Active infection somewhere in the body.
o Impairment of the extensor mechanism
o Serious chronic health problem
Relative Contraindications
o Joint neuropathic pain
o Overlying skin inadequate for surgery.
o Obesity
o Serious mental illness, alcoholism, or substance abuse
o Inadequate bone material for repair
o Serious peripheral vascular disease (PVD)
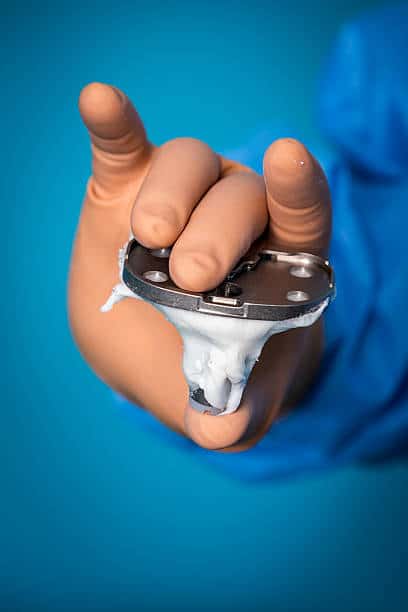
Equipment of Knee Replacement

Knee Replacement Surgery Cost
• Various femoral guides
• Various tibial guides
• Patella sizing guide
• Femoral component
• Tibial baseplate
• Patellar button
• Plastic bearing
How Knee Replacement is Performed?
The surgery is usually done under general anesthesia. Other types of anesthesia include spinal, epidural, or regional nerve block.
The steps of Knee Replacement are as follow:
Preparing the Joint
Broken cartilaginous surfaces on the femur and tibia endings, as well as a small fragment of bone under them, are excised.
Placing the Metallic Implant
Metallic components are used to replace the excised cartilage and bone, re-creating the joint’s surface. Metallic pieces can be glued or pressed-fit into the bone.
Patellar Resurfacing
With a plastic screw, the undersurface of the patella is sliced and resurfaced. Based on the circumstances, sometimes, surgeons don’t need to resurface the kneecap.
Placing a Spacer
To produce a smoother sliding interface, a plastic spacer is put between the metallic components.
Risks of Knee Replacement
The following are all possible Complications of knee replacement
• Infection, superficial and deep
• Blood clot
• Pulmonary embolism
• Fracture
• Dislocation
• Instability
• Osteolysis resulting in component loosening
• Pain
• Stiffness
• Vascular injury
• Nerve injury
How Long Does a Knee Replacement Last?
The majority of knee replacement surgeries take between 1 into 2 hours to complete. but you should remain in the theater for 2 hours under observation
Cost of Knee Replacement
In a few studies, knee replacement surgery costs between $25,000 and $45,000 in the United States in 2020.
See Also
References
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507914/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3382388/
https://www.hss.edu/condition-list_knee-replacement.asp

Dr.Sharif Samir Alijla, is a general medical doctor and a well-rounded professional that cares and treats patients from Palestine. I participated in many medical studies and conferences, I've launched a range of community initiatives and taken part in a variety of leadership and change training programs. I worked as an author for many medical websites such as TebFact . I specialized in writing medical articles from authoritative and updated sources in a simple and smooth the way for the reader.